Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C
CNguyen, B. V. C.*; 村上 健太*; Chena, L.*; Phongsakorn, P. T.*; Chen, X.*; 橋本 貴司; Hwang, T.*; 古澤 彰憲; 鈴木 達也*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 39, p.101639_1 - 101639_9, 2024/06
In reactor pressure vessel materials, the formation of Mn- and Ni-rich nanoclusters is a major cause of neutron irradiation embrittlement. The segregation of these solute atoms into dislocation loops has attracted attention as a mechanism to accelerate solute clustering. In this study, the behaviors of solute Mn and Ni atoms in Fe-0.6wt.%Ni, Fe-1.4wt.%Mn, and Fe-1.4wt.%Mn-0.6wt.%Ni alloys irradiated at 400  C up to 3 dpa were analyzed using three-dimensional atom probe tomography. Solute atom clusters were observed in all materials, and their shapes were spherical, flat, and torus in FeNi, FeMn, and FeMnNi, respectively. In ternary alloy FeMnNi, Mn and Ni atoms were concentrated in the sample in the form of arcs, and the orientation of the plane containing the arcs was estimated by comparing field desorption images. The size, number density, and orientation of this structure were found to be in good agreement with those of both types of dislocation loops, namely, b = 1/2
C up to 3 dpa were analyzed using three-dimensional atom probe tomography. Solute atom clusters were observed in all materials, and their shapes were spherical, flat, and torus in FeNi, FeMn, and FeMnNi, respectively. In ternary alloy FeMnNi, Mn and Ni atoms were concentrated in the sample in the form of arcs, and the orientation of the plane containing the arcs was estimated by comparing field desorption images. The size, number density, and orientation of this structure were found to be in good agreement with those of both types of dislocation loops, namely, b = 1/2  111
111 and b =
and b =  100
100 , identified in a previous study using the same material. The positions of Ni and Mn enrichment did not fully overlap. Ni atoms tended to be concentrated more in the inner part of the loop than the Mn atoms. Mn atoms were enriched only in the vicinity of the dislocation loops, whereas Ni atoms showed a higher concentration inside the dislocation loops than in the bulk.
, identified in a previous study using the same material. The positions of Ni and Mn enrichment did not fully overlap. Ni atoms tended to be concentrated more in the inner part of the loop than the Mn atoms. Mn atoms were enriched only in the vicinity of the dislocation loops, whereas Ni atoms showed a higher concentration inside the dislocation loops than in the bulk.
Lu, K.; 高見澤 悠; Li, Y.; 眞崎 浩一*; 高越 大輝*; 永井 政貴*; 南日 卓*; 村上 健太*; 関東 康祐*; 八代醍 健志*; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.22-00484_1 - 22-00484_13, 2023/08
A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code, PASCAL, has been developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency for failure probability and failure frequency evaluation of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and thermal transients. To strengthen the applicability of PASCAL, considerable efforts on verifications of the PASCAL code have been made in the past years. As a part of the verification activities, a working group consisted of different organizations from industry, universities and institutes, was established in Japan. In the early phase, the working group focused on verifying the PFM analysis functions for RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs) subjected to pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. Recently, the PASCAL code has been improved in order to run PFM analyses for both RPVs in PWRs and boiling water reactors (BWRs) subjected to a broad range of transients. Simultaneously, the working group initiated a verification plan for the improved PASCAL through independent PFM analyses by different organizations. Concretely, verification analyses for a PWR-type RPV subjected to PTS transients and a BWR-type RPV subjected to a low-temperature over pressure transient were performed using PASCAL. This paper summarizes those verification activities, including the verification plan, analysis conditions and results. Based on the verification studies, the reliability of PASCAL for probabilistic integrity assessments of Japanese RPVs was confirmed with confidence.
Lu, K.; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 199, p.104706_1 - 104706_13, 2022/10
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:60.63(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL was developed in Japan for probabilistic integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) in pressurized water reactors (PWRs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) transients. To strengthen the practical applications of PFM methodology in Japan, PASCAL has been upgraded to a new version, PASCAL5, which enables PFM analyses of RPVs in both PWRs and boiling water reactors (BWRs) subjected to a broad range of transients, including PTS and normal operational transients. In this paper, the recent improvements in PASCAL5 are described such as the incorporated stress intensity factor solutions and corresponding calculation methods for external surface cracks and embedded cracks near the RPV outer surface. In addition, the analysis conditions and evaluation models recommended for PFM analyses of Japanese RPVs in BWRs are investigated. Finally, PFM analysis examples for core region of a Japanese BWR-type model RPV subjected to two transients (i.e., low-temperature over pressure and heat-up transients) are presented using PASCAL5.
岩田 景子; 端 邦樹; 飛田 徹; 廣田 貴俊*; 高見澤 悠; 知見 康弘; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/07
The crack arrest fracture toughness, K , values for highly-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels are estimated according to a linear relationship between crack arrest toughness reference temperature, T
, values for highly-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels are estimated according to a linear relationship between crack arrest toughness reference temperature, T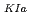 , and the temperature corresponding to a fixed arrest load, equal to 4 kN, T
, and the temperature corresponding to a fixed arrest load, equal to 4 kN, T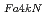 , obtained by instrumented Charpy impact test. The relationship between T
, obtained by instrumented Charpy impact test. The relationship between T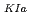 derived from the instrumented Chrapy impact test and fracture toughness reference temperature, T
derived from the instrumented Chrapy impact test and fracture toughness reference temperature, T , was expressed as an equation proposed in a previous report. The coefficients in the equation could be fine-tuned to obtain a better fitting curve using the present experimental data and previous K
, was expressed as an equation proposed in a previous report. The coefficients in the equation could be fine-tuned to obtain a better fitting curve using the present experimental data and previous K data. The K
data. The K curve for RPV;A533B class1 steels irradiated up to 1.3
curve for RPV;A533B class1 steels irradiated up to 1.3 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV) was compared with a K
1 MeV) was compared with a K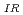 curve defined in JEAC4206-2016. It was shown that the K
curve defined in JEAC4206-2016. It was shown that the K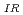 curve was always lower than the 1%ile curve of K
curve was always lower than the 1%ile curve of K for these irradiated RPV steels. This result indicates that the conservativeness of the method defined in JEAC4206-2016 to evaluate K
for these irradiated RPV steels. This result indicates that the conservativeness of the method defined in JEAC4206-2016 to evaluate K using K
using K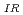 curve is confirmed for highly-irradiated RPV steels.
curve is confirmed for highly-irradiated RPV steels.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; 吉村 忍*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(2), p.021505_1 - 021505_8, 2021/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:10.51(Engineering, Mechanical)Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is considered to be a promising methodology in structural integrity assessments of pressure-boundary components in nuclear power plants since it can rationally represent the inherent probabilistic distributions for influence parameters without over-conservativeness. To strengthen the applicability of PFM methodology in Japan, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a PFM analysis code PASCAL4 which enables the failure frequency evaluation of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and thermal transients. PASCAL4 is expected to make a significant contribution to the probabilistic integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs. In this study, PFM analysis for a Japanese model RPV in a pressurized water reactor (PWR) was conducted using PASCAL4, and the effects of nondestructive examination (NDE) and neutron flux reduction on failure frequencies of the RPV were quantitatively evaluated. From the analysis results, it is concluded that PASCAL4 is useful for probabilistic integrity assessments of embrittled RPVs and can enhance the applicability of PFM methodology.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(5), p.051501_1 - 051501_10, 2020/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:15.81(Engineering, Mechanical)Structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) is essential for the safe operation of nuclear power plants. For RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs), the assessment should be performed by considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. To assess the structural integrity of an RPV, a traditional method is usually employed by comparing fracture toughness of the RPV material with the stress intensity factor ( ) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,
) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,  of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on
of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on  calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for
calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for  calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.
calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2020) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2020/08
In Japan, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code, PASCAL4, for probabilistic evaluation of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) in pressurized water reactors (PWRs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. Besides severe PTS events, however, transients associated with normal operations, such as the cooldown and heatup transients associated with reactor shutdown and startup, respectively, should also be considered in the integrity assessment of RPVs in both PWRs and boiling water reactors (BWRs). With regard to a heatup transient, because temperature is at its minimum, and tensile stress at its maximum on the RPV outer surface, outer surface crack and embedded crack near the RPV outer surface should be taken into account. To extend the applicability of PASCAL4, we improved the code to include analysis functions for these cracks. The improved PASCAL4 can be used to run PFM analyses of RPVs subjected to both cooldown (including PTS) and heatup transients. In this paper, improvements made to PASCAL4 are firstly described, including the incorporated stress intensity factor solutions and the corresponding calculation methods for vessel outer surface crack and embedded crack near the outer surface. Using the improved PASCAL4, PFM analysis examples for a Japanese BWR-type model RPV subjected to thermal transients including a low temperature overpressure event and a heatup transient are presented.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; 宮本 裕平*; 廣田 貴俊*; 板橋 遊*; 永井 政貴*; 鈴木 雅秀*; 関東 康祐*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00573_1 - 19-00573_14, 2020/06
Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is considered a promising methodology in assessing the integrity of structural components in nuclear power plants because it can rationally represent the influence parameters in their probabilistic distributions without over-conservativeness. In Japan, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a PFM analysis code PASCAL4 (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWRs Version 4) which enables the probabilistic integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock events. Several efforts have been made to verify PASCAL4 to ensure that this code can provide reliable analysis results. In particular, a Japanese working group, which consists of different participants from the industry and from universities and institutes, has been established to conduct the verification studies. This paper summarizes verification activities of the working group in the past two years. Based on those verification activities, the reliability and applicability of PASCAL4 for structural integrity assessments of Japanese RPVs have been confirmed with great confidence.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(2), p.021208_1 - 021208_11, 2020/04
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:42.63(Engineering, Mechanical)In Japan, a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL was developed for structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. By reflecting the latest knowledge and findings, the evaluation functions are continuously improved and have been incorporated into PASCAL4 which is the most recent version of the PASCAL code. In this paper, the improvements made in PASCAL4 are explained in detail, such as the evaluation model of warm prestressing (WPS) effect, evaluation function of confidence levels for PFM analysis results by considering the epistemic and aleatory uncertainties in probabilistic variables, the recent stress intensity factor (KI) solutions, and improved methods for KI calculations when considering complicated stress distributions. Moreover, using PASCAL4, PFM analysis examples considering these improvements are presented.
勝山 仁哉; 小坂部 和也*; 宇野 隼平*; Li, Y.; 吉村 忍*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(2), p.021205_1 - 021205_10, 2020/04
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:15.81(Engineering, Mechanical)確率論的破壊力学(PFM)に基づく構造健全性評価手法は、経年劣化に関連する様々な因子の確率分布を考慮して原子炉圧力容器(RPV)の破損頻度を評価できる合理的な手法である。我々は、中性子照射脆化や加圧熱衝撃事象(PTS)事象を考慮してRPVの破損頻度を評価するPFM解析コードPASCALを開発してきた。また、国内におけるPFMの適用性向上を図るため、破壊力学に関する知識を有する解析者がそれを参照することでPFM解析を行い亀裂貫通頻度を評価できるよう、標準的解析要領を整備した。本要領は、本文、解説及び付属書で構成されており、PFM解析に関する技術的根拠や最新知見が取りまとめられたものになっている。本論では、本要領の概要について述べるとともに、本要領とPTS評価に関する国内データベースに基づき得られた国内モデルRPVに対する破損頻度の評価結果について述べる。
相原 純; 後藤 実; 植田 祥平; 橘 幸男
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-018, 22 Pages, 2020/01
Pu燃焼高温ガス炉とは、再処理Puの量を安全に減らすための高温ガス炉である。Pu燃焼高温ガス炉では、PuO -YSZの微小球にZrC層を被覆し、更にSiC-TRISO被覆を施したCFPを用いる計画である。ZrC層の役割は、酸素ゲッターである。主に、このPu燃焼高温ガス炉のCFPにも適用するための現時点で可能な範囲での準備として、高温ガス炉の燃料であるCFPの内圧破損確率評価のための、健全CFPの被覆層の応力計算用コードシステムであるCode-B-2を改良し、Code-B-2.5.2とした。本報告では、Code-B-2.5.2の基礎式を報告する。
-YSZの微小球にZrC層を被覆し、更にSiC-TRISO被覆を施したCFPを用いる計画である。ZrC層の役割は、酸素ゲッターである。主に、このPu燃焼高温ガス炉のCFPにも適用するための現時点で可能な範囲での準備として、高温ガス炉の燃料であるCFPの内圧破損確率評価のための、健全CFPの被覆層の応力計算用コードシステムであるCode-B-2を改良し、Code-B-2.5.2とした。本報告では、Code-B-2.5.2の基礎式を報告する。
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; 吉村 忍*
Proceedings of 2019 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2019) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2019/07
Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) methodology, which represents the influence parameters in their inherent probabilistic distributions, is deemed to be promising in the structural integrity assessment of pressure-boundary components in nuclear power plants. To strengthen the applicability of PFM methodology in Japan, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a PFM analysis code called PASCAL4 (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWRs Version 4) which can be used to evaluate the failure frequency of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock events. PASCAL4 is expected to make a significant contribution to the probabilistic integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs. In this study, PFM analyses are performed for a Japanese model RPV using PASCAL4, and the effects of non-destructive examination and neutron fluence mitigation on failure frequency of RPV are quantitatively evaluated. From the analysis results, it is concluded that PASCAL4 is useful for the structural integrity assessment of RPVs and can enhance the applicability of PFM methodology.
勝山 仁哉; 眞崎 浩一; Lu, K.; 渡辺 正*; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2019 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2019) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/07
加圧水型原子炉の原子炉圧力容器(RPV)において、非常用炉心冷却系(ECCS)の冷却材の温度が加圧熱衝撃(PTS)事象時のRPVの構造健全性に影響する可能性がある。PTS事象時の熱衝撃の影響を低減することを目的とした緩和措置として、ECCSの冷却水温度を上げることに着目し、国内の代表的な高経年化したPWRプラントを対象に、システム解析コードRELAP5及び確率論的破壊力学(PFM)解析コードPASCAL4を用いた熱水力解析及びPFM解析を実施した。その結果、高圧注入系と低圧注入系(HPI/LPI)の冷却水温度のみを上昇させた場合には破損確率の低減に効果はない。一方、HPI/LPI及び蓄圧系の冷却水温度を上昇させた場合にはRPVの破損確率が大きく低減することを示した。
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; 宮本 裕平*; 廣田 貴俊*; 板橋 遊*; 永井 政貴*; 鈴木 雅秀*; 関東 康祐*
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2019/05
Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is considered as a promising methodology in the integrity assessment of structural components in a nuclear power plant since it can rationally represent the influence parameters in their inherent probabilistic distributions without over-conservativeness. In Japan, a PFM analysis code called PASCAL4 (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWRs Version 4) has been developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency, which can be used for structural integrity assessments of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock events. Up till now, many efforts have been made on verifying the PASCAL4 code. Among them, a Japanese working group which is consisted of seven participants from industries, universities and institutes was established to conduct the verification studies. Based on verification activities during the past two years, the reliability and applicability of PASCAL4 for structural integrity assessments of Japanese RPVs were confirmed with great confidence. This paper summarizes the verification activities in this working group including the verification plan, analysis conditions and results.
伊藤 主税; 内藤 裕之; 石川 高史; 伊藤 敬輔; 若井田 育夫
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011038_1 - 011038_6, 2019/01
東京電力ホールディングス福島第一原子力発電所の原子炉圧力容器と格納容器の内部調査への適用を想定して、光ファイバーの耐放射線性を向上させた。原子炉圧力容器内の線量率として想定されている~1kGy/hレベルの放射線環境に適用できるよう、OH基を1000ppm含有した溶融石英コアとフッ素を4%含有した溶融石英クラッドからなるイメージ用光ファイバを開発し、光ファイバをリモートイメージング技術に応用することを試みた。イメージファイバの本数は先行研究時の2000本から実用レベルの22000本に増加させた。1MGyのガンマ線照射試験を行った結果、赤外線画像の透過率は照射による影響を受けず、視野範囲の空間分解能の変化も見られなかった。これらの結果、耐放射線性を向上させたイメージファイバを用いたプロービングシステムの適用性が確認できた。
飛田 徹; 西山 裕孝; 鬼沢 邦雄
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-013, 60 Pages, 2018/11
原子炉圧力容器の健全性を判断する上で、破壊靱性をはじめとする材料の機械的特性は重要な情報となる。本レポートは、日本原子力研究開発機構が取得した中性子照射材を含む原子炉圧力容器鋼材の機械的特性、具体的には引張試験, シャルピー衝撃試験, 落重試験及び破壊靱性試験の公開データをまとめたものである。対象とした材料は、初期プラントから最新プラント相当の不純物含有量及び靱性レベルで製造されたJIS SQV2A(ASTM A533B Class1)相当の5種類の原子炉圧力容器鋼である。また母材に加え、原子炉圧力容器の内張りとして用いられている2種類のステンレスオーバーレイクラッド材の機械的特性データについても記載した。これらの機械的特性データは、材料ごとにグラフで整理するとともに今後のデータの活用しやすさを考慮して表形式でリスト化した。
Lu, K.; 眞崎 浩一; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2018 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2018), 8 Pages, 2018/07
In Japan, a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency for structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). The most recent release is PASCAL Version 4 (hereafter, PSACAL4) which can be used to evaluate the failure frequency of RPVs considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock events. For the integrity assessment of RPVs, development of crack evaluation models is important. In this study, finite element analyses are performed firstly to verify the stress intensity factor calculations of cracks in PASCAL4. In addition, the applicability of the crack evaluation models in PASCAL4 such as the location of embedded cracks, crack shape and depth of surface cracks, and the increment of crack propagation is investigated. Based on sensitivity analyses of crack evaluation models for Japanese RPVs using PASCAL4, the effects of these evaluation models on failure frequency are clarified. From the analysis results, crack evaluation models recommended to the failure frequency evaluation for a Japanese model RPV are discussed.
Lu, K.; 眞崎 浩一; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; 宇野 隼平*
Proceedings of 2018 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2018), 10 Pages, 2018/07
In Japan, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a PFM analysis code PASCAL (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWRs) for structural integrity assessment of Japanese reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock transients. By reflecting the latest knowledge and findings, the PASCAL code has been continuously improved. In this paper, the development of PASCAL Version 4 (hereafter, PASCAL4) is described. Several analysis functions incorporated into PASCAL4 for evaluating the failure frequency of RPVs are introduced, for example, the evaluation function of confidence level of failure frequency considering epistemic and aleatory uncertainties in probabilistic variables, the recent stress intensity factor (KI) solutions and KI calculation methods considering complicated stress distributions, and the recent Japanese irradiation embrittlement prediction method. Finally, using PASCAL4, a PFM analysis example for a Japanese model RPV is presented.
知見 康弘; 岩田 景子; 飛田 徹; 大津 拓与; 高見澤 悠; 吉本 賢太郎*; 村上 毅*; 塙 悟史; 西山 裕孝
JAEA-Research 2017-018, 122 Pages, 2018/03
原子炉圧力容器の加圧熱衝撃(Pressurized Thermal Shock: PTS)事象に対する構造健全性評価に与える影響項目の一つである高温予荷重(Warm Pre-stress: WPS)効果は、高温時に予め荷重を受けた場合に、冷却中の荷重減少過程では破壊が生じず、低温での再負荷時の破壊靱性が見かけ上増加する現象である。WPS効果については、主として弾性データによって再負荷時の見かけの破壊靱性を予測するための工学的評価モデルが提案されているが、試験片の寸法効果や表面亀裂に対して必要となる弾塑性評価は考慮されていない。本研究では、実機におけるPTS時の過渡事象を模擬した荷重-温度履歴を与える試験(WPS効果確認試験)を行い、WPS効果に対する試験片寸法や荷重-温度履歴の影響を確認するとともに、工学的評価モデルの検証を行った。再負荷時の見かけの破壊靭性について、予荷重時の塑性の程度が高くなると試験結果は工学的評価モデルによる予測結果を下回る傾向が見られた。比較的高い予荷重条件に対しては、塑性成分等を考慮することにより工学的評価モデルの高精度化が可能となる見通しが得られた。
荒井 健作*; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2017/11
原子力機構が開発した確率論的破壊力学(PFM)解析コードPASCAL及び米国のPFM解析コードFAVORを用いて、米国3ループ加圧水型原子炉の原子炉圧力容器を対象としたベンチマーク解析を実施した。応力拡大係数の式等の解析条件を一致させた結果、両コードの解析結果は良好に一致した。